Sunless tanning
Can I really get a tan without exposure to UV rays? Safely?
"Sunless tanning", "self-tanning", "being tangoed", or even "UV-free tanning" refers to the application of chemicals to the skin in a cream base to produce an effect similar in appearance to a traditional suntan obtained from the direct sun's rays.
This process provides a temporary, artificial tan claimed to be non-toxic and skin safe, without the potential risks associated with UV exposure, such as skin cancer. The tan is temporary and will fade gradually over 3 to 10 days.
The original idea seems to have started primarily as a response to increasing links between exposing your skin to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays and the increased incidences of skin cancer. This in turn gave rise to other alternatives such as the use of a sun bed, or tanning bed.
 Stay out of the sun cancer warning
Stay out of the sun cancer warningRelated topics
Artificial tanning
Tanning bed lotions
Effects of tanning beds
Lotions for sunless tans
Tanning bed supplies
Products for tanning without sun
Tanning bed dangers
Self Tanning Lotion
Tanning bed tips
Discount tanning bed lotion
Tanning bed safety
Pregnancy and tanning bed use
Top sunless tanning advice
Neutrogena tanning lotion
Best sunless tanning Lotions
Used tanning beds
Skin cancer from tanning beds
How does Sunless Tanning actually work?
The skin is made up of two main layers:
- the epidermis on the outside
- the dermis on the inside
When you are talking about tanning, the epidermis is where the action happens and the epidermis itself also consists of layers. The deepest layer of the epidermis, called the stratum basal (basal layer), is affected during a sun tanning process.
However, the stratum corneum (horny layer) is the outermost layer of the epidermis and it is this layer that is affected by most sunless tanning products.
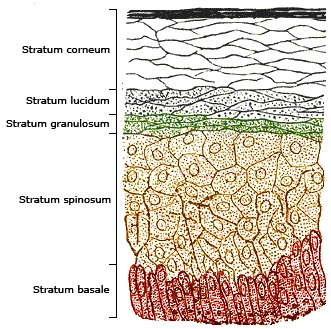 diagram to illustrate the layers of the skin
diagram to illustrate the layers of the skinThe only color additive currently approved by the FDA for these sunless tanner creams is an ingredient called dihydroxyacetone (DHA)
It does not contain a dye, stain or paint, but causes a chemical reaction with the amino acids in the dead layer on the skin surface. This results in a browning or darkening of the skin.
This is actually similar to a reaction well known to food chemists called the Maillard reaction. Amusingly, this refers to the browning process during food manufacturing and storage that is similar to the grilled sausages below!
Great care in application of sunless tanning creams is important as a smooth, even application of the cream can be difficult. Plus, some areas of the skin can react differently to the cream. This can mean a very unevenly tanned effect is the result.
 Maillard Reaction seen in these cooked sausages
Maillard Reaction seen in these cooked sausagesVit D not created with sunless tanning
So this chemical reaction does not involve skin pigmentation and it does not need exposure to Ultra Violet rays to initiate the colour change in your skin. DHA is actually a colourless sugar that interacts with the dead skin cells located in the stratum corner of the epidermis. As the sugar interacts with these dead skin cells, a color change occurs.
This change usually lasts about five to seven days from the initial application. Every day, millions of dead skin cells are sloughed off or worn away from the surface of your skin. In fact, every 35 to 45 days, you have an entirely new epidermis.
This is why tans from sunless, as well as self-tanning lotions, will gradually fade. As the dead cells are worn away, so is your tan. For this reason, most of the sunless tanning products suggest that you reapply them every three days or so to maintain your "tan".
However, what this tan doesn't allow you is the Vitamin D benefit created when exposed to the sun's UVB rays.




New! Comments
Have your say... please leave me a comment in the box below.